LEADERSHIP


Leadership in business is the
capacity of a company's management to set and achieve challenging goals, take
fast and decisive action when needed, outperform the competition, and inspire
others to perform at the highest level they can.
Leadership is a process by which an
executive can direct, guide and influence the behavior and work of others
towards accomplishment of specific goals in a given situation. Leadership is
the ability of a manager to induce the subordinates to work with confidence and
zeal.
Leadership is the potential to
influence behaviour of others. It is also defined as the capacity to influence
a group towards the realization of a goal. Leaders are required to develop
future visions, and to motivate the organizational members to want to achieve
the visions.
It can be difficult to place a value
on leadership or other qualitative aspects of a company, versus quantitative
metrics that are commonly tracked and much easier to compare between companies.
Leadership can also speak to a more holistic approach, as in the tone a
company's management sets or the culture of the company that management
establishes.
According to Keith Davis, “Leadership is the ability to persuade others to seek
defined objectives enthusiastically. It is the human factor which binds a group
together and motivates it towards goals.”
Characteristics
of Leadership
- It is a inter-personal process in which a manager is into influencing and guiding workers towards attainment of goals.
- It denotes a few qualities to be present in a person which includes intelligence, maturity and personality.
- It is a group process. It involves two or more people interacting with each other.
- A leader is involved in shaping and moulding the behaviour of the group towards accomplishment of organizational goals.
- Leadership is situation bound. There is no best style of leadership. It all depends upon tackling with the situations.
Understanding
Leadership
Leadership provides direction for a
company and its workers. Employees need to know the direction in which the
company is headed and who to follow to reach the destination. Leadership
involves showing workers how to effectively perform their responsibilities and
regularly supervising the completion of their tasks.
Leadership is also about setting a
positive example for staff to follow, by being excited about the work, being
motivated to learn new things, and helping out as needed in both individual and
team activities.
How
Leadership Works
Effective leadership includes
exhibiting a strong character. Leaders exhibit honesty, integrity,
trustworthiness, and ethics. Leaders act in line with how they speak and earn
the right to be responsible for others’ success in the company.
Strong leadership involves clear
communication skills. Leaders speak with and listen to staff members, respond
to questions and concerns, and are empathetic. Leaders use effective
communication skills for moving the company forward and achieving new levels of
success.
True leadership sees where the
company is headed and plans the steps needed to get there. Visualizing what is
possible, following trends in the industry, and taking risks to grow the
business are all required of leaders.
Productive leadership shows optimism
and provides positive energy for staff. Good leaders are supportive and are
truly concerned about the well-being of others. Leaders find answers to
challenges and reassure and inspire workers when things go awry. Leaders find
ways for staff to work together and achieve maximum results in an efficient and
effective manner.
Importance of Leadership
Leadership is an important function
of management which helps to maximize efficiency and to achieve organizational
goals. The following points justify the importance of leadership in a concern.
- Initiates action- Leader is a person who starts the work by communicating the policies and plans to the subordinates from where the work actually starts.
- Motivation- A leader proves to be playing an incentive role in the concern’s working. He motivates the employees with economic and non-economic rewards and thereby gets the work from the subordinates.
- Providing guidance- A leader has to not only supervise but also play a guiding role for the subordinates. Guidance here means instructing the subordinates the way they have to perform their work effectively and efficiently.
- Creating confidence- Confidence is an important factor which can be achieved through expressing the work efforts to the subordinates, explaining them clearly their role and giving them guidelines to achieve the goals effectively. It is also important to hear the employees with regards to their complaints and problems.
- Building morale- Morale denotes willing co-operation of the employees towards their work and getting them into confidence and winning their trust. A leader can be a morale booster by achieving full co-operation so that they perform with best of their abilities as they work to achieve goals.
- Builds work environment- Management is getting things done from people. An efficient work environment helps in sound and stable growth. Therefore, human relations should be kept into mind by a leader. He should have personal contacts with employees and should listen to their problems and solve them. He should treat employees on humanitarian terms.
- Co-ordination- Co-ordination can be achieved through reconciling personal interests with organizational goals. This synchronization can be achieved through proper and effective co-ordination which should be primary motive of a leader.

Role of a Leader
Following are the main roles of a
leader in an organization :
- Required at all levels- Leadership is a function which is important at all levels of management. In the top level, it is important for getting co-operation in formulation of plans and policies. In the middle and lower level, it is required for interpretation and execution of plans and programmes framed by the top management. Leadership can be exercised through guidance and counseling of the subordinates at the time of execution of plans.
- Representative of the organization- A leader, i.e., a manager is said to be the representative of the enterprise. He has to represent the concern at seminars, conferences, general meetings, etc. His role is to communicate the rationale of the enterprise to outside public. He is also representative of the own department which he leads.
- Integrates and reconciles the personal goals with organizational goals- A leader through leadership traits helps in reconciling/ integrating the personal goals of the employees with the organizational goals. He is trying to co-ordinate the efforts of people towards a common purpose and thereby achieves objectives. This can be done only if he can influence and get willing co-operation and urge to accomplish the objectives.
- He solicits support- A leader is a manager and besides that he is a person who entertains and invites support and co-operation of subordinates. This he can do by his personality, intelligence, maturity and experience which can provide him positive result. In this regard, a leader has to invite suggestions and if possible implement them into plans and programmes of enterprise. This way, he can solicit full support of employees which results in willingness to work and thereby effectiveness in running of a concern.
- As a friend, philosopher and guide- A leader must possess the three dimensional traits in him. He can be a friend by sharing the feelings, opinions and desires with the employees. He can be a philosopher by utilizing his intelligence and experience and thereby guiding the employees as and when time requires. He can be a guide by supervising and communicating the employees the plans and policies of top management and secure their co-operation to achieve the goals of a concern. At times he can also play the role of a counselor by counseling and a problem-solving approach. He can listen to the problems of the employees and try to solve them.
Qualities of a Leader
A leader has got multidimensional
traits in him which makes him appealing and effective in behavior. The
following are the requisites to be present in a good leader:
- Physical appearance- A leader must have a pleasing appearance. Physique and health are very important for a good leader.
- Vision and foresight- A leader cannot maintain influence unless he exhibits that he is forward looking. He has to visualize situations and thereby has to frame logical programmes.
- Intelligence- A leader should be intelligent enough to examine problems and difficult situations. He should be analytical who weighs pros and cons and then summarizes the situation. Therefore, a positive bent of mind and mature outlook is very important.
- Communicative skills- A leader must be able to communicate the policies and procedures clearly, precisely and effectively. This can be helpful in persuasion and stimulation.
- Objective- A leader has to be having a fair outlook which is free from bias and which does not reflects his willingness towards a particular individual. He should develop his own opinion and should base his judgement on facts and logic.
- Knowledge of work- A leader should be very precisely knowing the nature of work of his subordinates because it is then he can win the trust and confidence of his subordinates.
- Sense of responsibility- Responsibility and accountability towards an individual’s work is very important to bring a sense of influence. A leader must have a sense of responsibility towards organizational goals because only then he can get maximum of capabilities exploited in a real sense. For this, he has to motivate himself and arouse and urge to give best of his abilities. Only then he can motivate the subordinates to the best.
- Self-confidence and will-power- Confidence in himself is important to earn the confidence of the subordinates. He should be trustworthy and should handle the situations with full will power. (You can read more about Self-Confidence at : Self Confidence - Tips to be Confident and Eliminate Your Apprehensions).
- Humanist-This trait to be present in a leader is essential because he deals with human beings and is in personal contact with them. He has to handle the personal problems of his subordinates with great care and attention. Therefore, treating the human beings on humanitarian grounds is essential for building a congenial environment.
- Empathy- It is an old adage “Stepping into the shoes of others”. This is very important because fair judgement and objectivity comes only then. A leader should understand the problems and complaints of employees and should also have a complete view of the needs and aspirations of the employees. This helps in improving human relations and personal contacts with the employees.
From the above qualities present in
a leader, one can understand the scope of leadership and it’s importance for
scope of business. A leader cannot have all traits at one time. But a few of
them helps in achieving effective results.
Leadership and Management - Relationship &
Differences
Leadership and management are the
terms that are often considered synonymous. It is essential to understand that
leadership is an essential part of effective management. As a crucial component
of management, remarkable leadership behaviour stresses upon building an
environment in which each and every employee develops and excels. Leadership is
defined as the potential to influence and drive the group efforts towards the
accomplishment of goals. This influence may originate from formal sources, such
as that provided by acquisition of managerial position in an organization.
A manager must have traits of a
leader, i.e., he must possess leadership qualities. Leaders develop and begin
strategies that build and sustain competitive advantage. Organizations require
robust leadership and robust management for optimal organizational efficiency.
Differences
between Leadership and Management
Leadership differs from management
in a sense that:
- While managers lay down the structure and delegates authority and responsibility, leaders provides direction by developing the organizational vision and communicating it to the employees and inspiring them to achieve it.
- While management includes focus on planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling; leadership is mainly a part of directing function of management. Leaders focus on listening, building relationships, teamwork, inspiring, motivating and persuading the followers.
- While a leader gets his authority from his followers, a manager gets his authority by virtue of his position in the organization.
- While managers follow the organization’s policies and procedure, the leaders follow their own instinct.
- Management is more of science as the managers are exact, planned, standard, logical and more of mind. Leadership, on the other hand, is an art. In an organization, if the managers are required, then leaders are a must/essential.
- While management deals with the technical dimension in an organization or the job content; leadership deals with the people aspect in an organization.
- While management measures/evaluates people by their name, past records, present performance; leadership sees and evaluates individuals as having potential for things that can’t be measured, i.e., it deals with future and the performance of people if their potential is fully extracted.
- If management is reactive, leadership is proactive.
- Management is based more on written communication, while leadership is based more on verbal communication.
The organizations which are over
managed and under-led do not perform upto the benchmark. Leadership
accompanied by management sets a new direction and makes efficient use of
resources to achieve it. Both leadership and management are essential for
individual as well as organizational success.
Leader versus Manager
“Leadership and managership are two
synonymous terms” is an incorrect statement. Leadership doesn’t require any
managerial position to act as a leader. On the other hand, a manager can be a
true manager only if he has got the traits of leader in him. By virtue of his
position, manager has to provide leadership to his group. A manager has to
perform all five functions to achieve goals, i.e., Planning, Organizing,
Staffing, Directing, and Controlling. Leadership is a part of these functions.
Leadership as a general term is not related to managership. A person can be a
leader by virtue of qualities in him. For example: leader of a club, class,
welfare association, social organization, etc. Therefore, it is true to say
that, “All managers are leaders, but all leaders are not managers.”
A leader is one who influences the
behavior and work of others in group efforts towards achievement of specified
goals in a given situation. On the other hand, manager can be a true manager
only if he has got traits of leader in him. Manager at all levels are expected
to be the leaders of work groups so that subordinates willingly carry
instructions and accept their guidance. A person can be a leader by virtue of
all qualities in him.
Leaders and Managers can be compared
on the following basis:
Basis
|
Manager
|
Leader
|
Origin
|
A person becomes a manager by
virtue of his position.
|
A person becomes a leader on basis
of his personal qualities.
|
Formal Rights
|
Manager has got formal rights in
an organization because of his status.
|
Rights are not available to a
leader.
|
Followers
|
The subordinates are the followers
of managers.
|
The group of employees whom the
leaders leads are his followers.
|
Functions
|
A manager performs all five
functions of management.
|
Leader influences people to work
willingly for group objectives.
|
Necessity
|
A manager is very essential to a
concern.
|
A leader is required to create
cordial relation between person working in and for organization.
|
Stability
|
It is more stable.
|
Leadership is temporary.
|
Mutual Relationship
|
All managers are leaders.
|
All leaders are not managers.
|
Accountability
|
Manager is accountable for self
and subordinates behaviour and performance.
|
Leaders have no well defined
accountability.
|
Concern
|
A manager’s concern is
organizational goals.
|
A leader’s concern is group goals
and member’s satisfaction.
|
Followers
|
People follow manager by virtue of
job description.
|
People follow them on voluntary
basis.
|
Role continuation
|
A manager can continue in office
till he performs his duties satisfactorily in congruence with organizational
goals.
|
A leader can maintain his position
only through day to day wishes of followers.
|
Sanctions
|
Manager has command over
allocation and distribution of sanctions.
|
A leader has command over
different sanctions and related task records. These sanctions are essentially
of informal nature.
|
Authority vs Leadership
The authority exercised is a kind of
legitimate power and people follow figures exercising it, because their
positions demand so irrespective of the person holding the position. Leaders
in organizations and elsewhere may have formal authorities but they mostly rely
on the informal authority that they exercise on people to influence them.
Leaders are trusted for their judgment and respected for their expertise,
integrity etc and hence followed and not because they hold a certain position.
For e.g. M.K. Gandhi for most part did not hold any official position to lead
the Indian freedom struggle.
It is also important to understand
that a formal authority and power emerging from it, might not always be able to
influence people in the desired manner as; in times of crisis and difficulties
people view it as coercion. On the other hand leadership tends to create
followers out of free will and choice without forcing them to accept anything
thrown their way. Authority rarely provides a scope for feedback, constructive criticism
or opinions of the people on whom it is exercised however leaders provide ample
platform to their followers to voice their thoughts and feedback.
When dealing with adults, the sole
use of authority to direct and discipline them hardly works, leadership
provides a better approach of sharing and involving thus building rapports with
followers and creating long term relationships. Authority can hardly make
people change their attitudes and behaviors with lasting effects and results
however a leader inspires followers through self modeled ways and hence
leadership displays greater effectiveness in addressing attitudes and behaviors
of people.
Exercising authority sometimes
limits the approaches to arrive at solutions for issues and problems while
leadership encourages people to look beyond the obvious and think innovatively
and sometimes emerge with radical solutions.
Apart from it, the biggest
difference between the two as cited by Stephen R Covey is the moral authority
held by leaders over the followers which is absent in the case of power from
authority. Within the organizational setup when leaders also have moral
authority on their subordinates by establishing a synchrony in their words and
actions; the rest of the structure and processes of the organization also get
aligned to it, thus creating a robust and transparent culture.
Authoritative way of working also
encourages individuals to work in silos while in the organizations of today;
the leaders need to have a complete picture and coordinate with other functions
and departments as and when required. It is indeed difficult for mangers and
leaders to move out of their circle of authority and coordinate and interact
with external people. However the need of the hour and the more effective
approach to leadership and management is when leaders come out of their comfort
zone and move from exercising authority on a small group to leading the entire
organization.
Individuals, who do not rely on
authority but lead people, are the ones who enjoy the privilege of their
ideologies and thoughts practiced by later generations long after they are gone. Even with individuals who held positions of
responsibilities, the ones who actually led their people are the ones
remembered and followed.
Leadership and Motivation
Motivation is a goal-oriented
characteristic that helps a person achieve his objectives. It pushes an
individual to work hard at achieving his or her goals. An executive must have
the right leadership traits to influence motivation. However, there is no
specific blueprint for motivation.
As a leader, one should keep an open
perspective on human nature. Knowing different needs of subordinates will
certainly make the decision-making process easier.
Both an employee as well as manager
must possess leadership and motivational traits. An effective leader must have
a thorough knowledge of motivational factors for others. He must understand the
basic needs of employees, peers and his superiors. Leadership is used as a
means of motivating others.
Given below are important guidelines
that outline the basic view of motivation:
- Harmonize and match the subordinate needs with the organizational needs. As a leader, the executive must ensure that the business has the same morals and ethics that he seeks in his employees. He should make sure that his subordinates are encouraged and trained in a manner that meets the needs of the business.
- Appreciation and rewards are key motivators that influence a person to achieve a desired goal. Rewarding good/ exceptional behavior with a small token of appreciation, certificate or letter can be a great motivator. If a certificate is awarded to a person, it should mention the particular act or the quality for which the individual is being rewarded.
- Being a role model is also a key motivator that influences people in reaching their goals. A leader should set a good example to ensure his people to grow and achieve their goals effectively.
- Encouraging individuals to get involved in planning and important issues resolution procedure not only motivates them, but also teaches the intricacies of these key decision-making factors. Moreover, it will help everyone to get better understanding of their role in the organization. The communication will be unambiguous and will certainly attract acknowledgement and appreciation from the leader.
- Developing moral and team spirit certainly has a key impact on the well-being of an organization. The metal or emotional state of a person constitutes his or her moral fabric. A leader’s actions and decisions affect the morale of his subordinates. Hence, he should always be aware of his decisions and activities. Team spirit is the soul of the organization. The leader should always make sure his subordinates enjoy performing their duties as a team and make themselves a part of the organization’s plans.
- A leader should step into the shoes of the subordinates and view things from subordinate’s angle. He should empathize with them during difficult times. Empathizing with their personal problems makes them stronger-mentally and emotionally.
- A meaningful and challenging job accomplished inculcates a sense of achievement among employees. The executive must make their employees feel they are performing an important work that is necessary for the organization’s well-being and success. This motivational aspect drives them to fulfill goals.
Remember, “To become an efficient
leader, you must be self-motivated”. You must know your identity, your
needs and you must have a strong urge to do anything to achieve your goals.
Once you are self-motivated, only then you can motivate others to achieve their
goals and to harmonize their personal goals with the common goals of the
organization.
Emotional Intelligence for Leaders
An organization is made up of people
and when people are involved, emotions automatically come into play, and a
workplace is no different. It would be unwise to assume that a workplace is all
objective, no-emotion only performance kind of a packed room where hormones
have no scope to creep in however the fact is that emotions alone are the
biggest motivator or de-motivator of an employee. The emotions alone, govern
the performance and efficiency of a worker and had it not been the case, we
would have never talked about the importance of work-life balance and for the
present context, the need of emotionally intelligent leaders.
The current times are very dynamic
not just economically but also socially where the social fabric is rapidly
evolving due to globalization and other influences. The average age of the
workforce is reducing and the leaders now look forward to managing people
belonging to different cultures and backgrounds. In such a situation, it is
important for a leader to be highly sensitized to the emotional aspects of
his/her transactions with people. Emotional Intelligence is basically the
ability to recognize and understand one’s own feelings and emotions as well as
those of others and use that information to manage emotions and relationships.
The 4 important aspects of EI as proposed by Daniel Goleman are:
- Self Awareness
- Self Management
- Social Awareness
- Relationship Management or Social Skills
A leader tends to have a huge
influence on the thoughts and motivation of people. He/she has the capacity to
enthuse optimism and confidence in the followers and lead them to constructive
endeavors which is called resonance and on the other hand they can negatively
influence them to destruct, e.g of such leaders being Hitler and d Osama Bin
Laden which is opposite to resonance called desonance.
Leaders are closely observed in
terms of their body language, facial expressions etc. So, it is important for a
leader to consider the non-verbal form of expressions as well, which may
positively or negatively influence followers. Therefore, if a leader is talking
about ethics in business with a slightly unconvinced and bemused look on his
face, the followers make a note of it and the message is not received by them.
A leader has to act as a role model too, supporting his statements, ideologies
and values with appropriate actions.
As a leader one also has to be aware
of one’s own capabilities and weaknesses, it is difficult to accept guidance
from a leader who is not self aware. As managers, leaders have to empathize as well
with the situations, emotions, aspirations and motivations of the subordinates.
A decreasing performance of a team member might be because of a number of
reasons, a disruptive worker might be facing motivation issues and a
subordinate who uses abusive language with others might be lacking confidence
in his own abilities. A leader needs to discern facts and try and reach to
deeper levels and understand things beyond obvious.
Apart from the above reasons,
Emotional Intelligence is also important because the followers or subordinate
expect it from their leaders. A subordinate working closely with the manager
would expect the manager to understand his situation and priorities. And not
surprisingly, whether manger does so or not, affects his level of commitment
and performance at work. A leader has to suitably know and understand when
he/she needs to be directive and when he needs to delegate. He/she needs to be
aware, when the team members are acting as one unit and when there are
differences.
It is sometimes awkward to address
emotional aspects of transactions between people but leaders need to understand
the importance and relevance of it as it has a huge impact on the performance
outcomes. While conducting reviews and development dialogues, the feedback has
to be delivered in a manner which is acceptable. The leader needs to be
sensitive to the insecurities and apprehensions of the subordinates which
sometimes might be expressed and sometimes kept undisclosed. At the senior
level it is all the more important as the senior executives find it hard to
clearly outline their anxieties and differences and the leader has to
anticipate some of them.
So, to be able to attract and retain
talented subordinates and keep them motivated, a leader needs to brush up on
his people skills and emotional intelligence, as all of them are not born with
the charisma to hold people. Fortunately, emotional intelligence with practice
and carefully directed efforts can be increased.
Organizational Leadership
Organizations need strong leadership
for optimum effectiveness. Leadership, as we know, is a trait which is both
inbuilt and can be acquired also. Organizational leadership deals with
both human psychology as well as expert tactics. Organizational leadership
emphasizes on developing leadership skills and abilities that are relevant
across the organizations. It means the potential of the individuals to face the
hard times in the industry and still grow during those times. It clearly identifies
and distinguishes the leaders from the managers. The leader should have
potential to control the group of individuals.
An ideal organizational leader
should not dominate over others. He should guide the individuals under him,
give them a sense of direction to achieve organizational goals successfully and
should act responsibly. He should be optimistic for sure. He should be
empathetic and should understand the need of the group members. An
organizational leader should not only lead others individually but also manage
the actions of the group.
Individuals who are highly
ambitious, have high energy level, an urge to lead, self-confidence,
intelligence, have thorough knowledge of job, are honest and flexible are more
likely to succeed as organizational leaders. Individuals who learn the
organizational leadership develop abilities and skills of teamwork, effective
communication, conflict resolution, and group problem solving techniques.
Organizational leaders clearly communicate organizational mission, vision and
policies; build employees morale, ensure efficient business operations; help
employees grow professionally and contribute positively towards organizations
mission.
Tips
for Effective Organizational Leadership
- A leader must lead himself, only then he can lead others. He must be committed on personal and professional front, and must be responsible. He must be a role model for others and set an example for them.
- A leader must boost up the morale of the employees. He should motivate them well so that they are committed to the organization. He should be well acquainted with them, have concern for them and encourage them to take initiatives. This will result in more efficient and effective employees and ensure organizational success.
- A leader must work as a team. He should always support his team and respect them. He should not hurt any employee. A true leader should not be too bossy and should not consider him as the supreme authority. He should realize that he is part of the organization as a whole.
Organizational leadership involves
all the processes and possible results that lead to development and achievement
of organizational goals. It includes employees’ involvement, genuineness,
effective listening and strategic communication.
Leadership Ethics - Traits of an Ethical Leader
Ethics refer to the desirable and
appropriate values and morals according to an individual or the society at
large. Ethics deal with the purity of individuals and their intentions. Ethics
serve as guidelines for analyzing “what is good or bad” in a specific scenario.
Correlating ethics with leadership, we find that ethics is all about the
leader’s identity and the leader’s role.
Ethical theories on leadership talk
about two main things: (a) The actions and behaviour of leaders; and (b) the
personality and character of leaders. It is essential to note that “Ethics
are an essential to leadership”. A leader drives and influences the
subordinates / followers to achieve a common goal, be it in case of team work,
organizational quest, or any project. It is an ethical job of the leader to
treat his subordinates with respect as each of them has unique personality. The
ethical environment in an organization is built and developed by a leader as
they have an influential role in the organization and due to the fact that
leaders have an influence in developing the organizational values.
An effective and ethical leader has
the following traits / characteristics:
1.
|
Dignity and respectfulness: He respects others. An ethical leader should not use his
followers as a medium to achieve his personal goals. He should respect their
feelings, decision and values. Respecting the followers implies listening
effectively to them, being compassionate to them, as well as being liberal in
hearing opposing viewpoints. In short, it implies treating the followers in a
manner that authenticate their values and beliefs.
|
2
|
Serving others: He serves others. An ethical leader should place his
follower’s interests ahead of his interests. He should be humane. He must act
in a manner that is always fruitful for his followers.
|
3
|
Justice: He is fair and just. An ethical leader must treat all his
followers equally. There should be no personal bias. Wherever some followers
are treated differently, the ground for differential treatment should be
fair, clear, and built on morality.
|
4
|
Community building: He develops community. An ethical leader considers his
own purpose as well as his followers’ purpose, while making efforts to
achieve the goals suitable to both of them. He is considerate to the
community interests. He does not overlook the followers’ intentions. He works
harder for the community goals.
|
5
|
Honesty: He is loyal and honest. Honesty is essential to be an
ethical and effective leader. Honest leaders can be always relied upon and
depended upon. They always earn respect of their followers. An honest leader
presents the fact and circumstances truly and completely, no matter how
critical and harmful the fact may be. He does not misrepresent any fact.
|
It is essential to note that
leadership is all about values, and it is impossible to be a leader if you lack
the awareness and concern for your own personal values. Leadership has a moral
and ethical aspect. These ethics define leadership. Leaders can use the above
mentioned traits as yardsticks for influencing their own behaviour.
Leadership Strategy - Which Leadership Style to Follow
?
Without an effective leadership
strategy, it is believed, that the organizational strategies do not work. Best
players in a team do not guarantee success without a great coach, similarly,
work teams may not function effectively if leaders do not follow an appropriate
leadership strategy.
To understand leadership styles here
are three scenarios:
Scenario 1 - A Teacher gives a question to the class full of students,
however, solves it for them;
Scenario 2 - A Teacher gives the question to the students and observes
how students solve them;
Scenario 3 - A Teacher gives a question to the students and moves
around the class, observes the students, and helps wherever required.
Scenario 1 was “Leading from the Front”,
Scenario 2 was “Supportive Leadership Style”, and Scenario 3 was “Interactive
Leadership Style”. Besides this the leadership styles / strategies could be
based on personality traits like Directive Leadership, Structured Leadership,
Intuitive Leadership, or Process Driven leadership.
Here are some tips while selecting
leadership strategy / style:
1
|
A leader must be aware of his / her
personality traits and those of his team members / followers to understand
which leadership style will be most effective.
|
2
|
A leader may not adopt a
consistent leadership all through his / her career. Situational Leadership
helps addressing varied needs / expectations of the followers as he the
leader adopts a strategy based on a situation he / she is in. In case a
leader has a self-reliant team, he needs to be using a directive leadership
style or lead form the front. He could instead delegate and provide inputs
where necessary.
|
3
|
A common mistake especially a lot
of new leaders make is to copy established / well know leaders. Remember,
each situation is unique and so are the followers. A leadership style which
may be suited to a well known leader may not be appropriate for your team.
Make no mistake here - do not try and imitate other leaders.
|
4
|
A leader will never be afraid of
trying new approach to solve a work problem or address a conflicting
situation. It is quite a possibility that a leader adopts a style that is not
by the book.
|
5
|
A leader must keep enhancing his /
her leadership skills. While on the job experience matters a lot, getting
enrolled into leadership courses after detailed evaluation of the program and
feedback of the participants will help implementing a leadership style more
effectively.
|
It is often said that good leaders
are born and not made; however, good leaders are those who are aware of their
personality traits and also of their followers. They know which leadership
style is to be adopted in a particular situation. Once this is done, there is a
little challenge left for a leader to become a “good / great” leader.
Leadership Styles - Important Leadership Styles
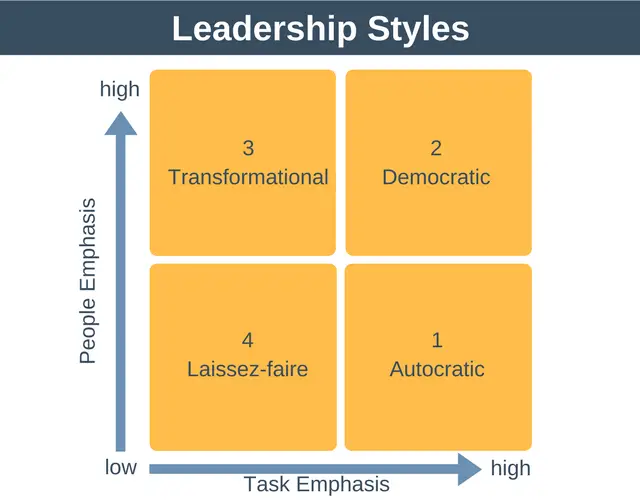

All leaders do not possess same
attitude or same perspective. As discussed earlier, few leaders adopt the
carrot approach and a few adopt the stick approach. Thus, all of the leaders do
not get the things done in the same manner. Their style varies. The leadership
style varies with the kind of people the leader interacts and deals with. A
perfect/standard leadership style is one which assists a leader in getting the
best out of the people who follow him.
Some of the important leadership
styles are as follows:
1
|
Autocratic leadership style: In this style of leadership, a leader has complete
command and hold over their employees/team. The team cannot put forward their
views even if they are best for the team’s or organizational interests. They
cannot criticize or question the leader’s way of getting things done. The
leader himself gets the things done. The advantage of this style is that it
leads to speedy decision-making and greater productivity under leader’s
supervision. Drawbacks of this leadership style are that it leads to greater
employee absenteeism and turnover. This leadership style works only when the
leader is the best in performing or when the job is monotonous, unskilled and
routine in nature or where the project is short-term and risky.
|
|
2
|
The Laissez Faire Leadership
Style: Here, the leader totally trusts
their employees/team to perform the job themselves. He just concentrates on
the intellectual/rational aspect of his work and does not focus on the
management aspect of his work. The team/employees are welcomed to share their
views and provide suggestions which are best for organizational interests.
This leadership style works only when the employees are skilled, loyal,
experienced and intellectual.
|
|
3
|
Democrative/Participative
leadership style: The leaders invite and encourage
the team members to play an important role in decision-making process, though
the ultimate decision-making power rests with the leader. The leader guides
the employees on what to perform and how to perform, while the employees
communicate to the leader their experience and the suggestions if any. The
advantages of this leadership style are that it leads to satisfied, motivated
and more skilled employees. It leads to an optimistic work environment and
also encourages creativity. This leadership style has the only drawback that
it is time-consuming.
|
|
4
|
Bureaucratic leadership: Here the leaders strictly adhere to the organizational
rules and policies. Also, they make sure that the employees/team also
strictly follows the rules and procedures. Promotions take place on the basis
of employees’ ability to adhere to organizational rules. This leadership
style gradually develops over time. This leadership style is more suitable
when safe work conditions and quality are required. But this leadership style
discourages creativity and does not make employees self-contented.
|
|
How to Create a Personal Leadership Brand ?
Every leader has a personal
leadership brand which might be carefully cultivated or intuitively perceived
by leaders themselves and their followers.
A personal leadership brand is an exclusive and a specific approach of a leader
to address challenges and manage his/her transactions with their subordinates
or followers. The best part of having a leadership brand is that it allows the
flexibility to the leaders to define their own leadership objectives and then
position themselves appropriately as per the need and situation. For example
Lee Iacocca promulgated a leadership brand which was resolute, determined,
persuasive and ready to take risks which helped him turn around Chrysler
similarly Gandhi’s leadership brand was that of integrity, honesty, principles,
strength of character and above all truth.
It is essential for a leader to
practice his/her leadership brand in thoughts and actions. How can a leader
build up a leadership brand if they do not have one already. A leadership brand
helps distinguish leaders and also outlines their approach, values, beliefs
etc.
- The first step definitely is identifying and establishing the results one wants to achieve by the end of a specific time period with a focus on preserving the interests of key stakeholders.
- The second step becomes those distinguishing features with which one wants to be known as a leader. For e.g. one might identify drive for result as one’s core strength area and can create a leadership brand based on the same
- The next step becomes defining your identity. One might chose two or three word phrases to define their approach to leadership like Innovating to Excel etc
- The last step becomes coming up with a leadership statement which conjuncts what one wants to be known for and what one wants to achieve
It is also important for leaders to
check their leadership brand with seniors, subordinates and other stake-holders
to understand their expectations from the role; and if any disconnect is
pointed out, it needs to be incorporated.
Apart from the above aspects,
leaders need to role model themselves and redefine their perceptions and
ambitions to encompass the entire institution, which they represent. A leader
needs to put the interests of the organization and stakeholders before his/her
personal ambition and goals and strive to create success which is sustainable
and does not need their constant presence.
The leaders need to understand that
a personal leadership brand cannot be created overnight but credibility is
earned the hard way, through years of perseverance. Once a leadership brand is created its acceptance and
stability is established only after results are achieved. So, if a leader
identifies certain goals but fails to achieve them, there are no takers for
that leadership brand, similarly if a leader displays behaviors contradictory
to what is outlined by his brand values, then also the credibility and respect
of the brand is lost.
Level 5 Leadership
We have always associated leadership
with a very visible and popular role which gives you recognition and a larger
than life status as a leader however the level 5 leadership proposes quite
opposing characteristics of a successful leader. Jim Collins and his research
team were exploring the factors that made good companies great way back in the
1960s. It was then that they stumbled upon the Level 5 leaders who were
invariably at the helm of affairs of all the companies which went on to become
great in their respective fields. Who exactly is a Level 5 leader? Collins
describes Level 5 leader as Humility + Will = Level 5. They are the nurturing
leaders who do not want credit but want success to sustain over a longer period
of time, long after they are gone.
Level 5 leaders are modest, shy and
fearless and possess the capability to transform an organization from good to
great without portraying themselves as wizards with magic wands. They prefer talking about the company and the contribution
of other people but rarely about their role or achievements. Let us have a look
at the hierarchical level of leadership identified:

The Level 5 leadership clearly
reestablishes the facts about a simply living and high thinking with an
emphasis on personal humility taught by the older generations. The financial
breakthroughs achieved by level 5 leaders prove that these characteristics can
achieve tangible results as well. The most important example in this context
can be cited of great world leaders like M.K. Gandhi and Abraham Lincoln, who
always put their vision ahead of their egos. They came across as shy and
defenseless people in their mannerism and speech but were hardly so when it
came to actions. The other example from the business leaders who fitted
perfectly into this category was Darwin E Smith who was the CEO of the paper
company Kimberly-Clark and turned it around to become the biggest consumer
paper product company. He was a unique mix of personal humility and will;
combined with risk taking ability which made him a role model for the business
leaders of today.
There are certain actions performed
by Level 5 leaders which separate them from the rest of the leaders and senior
executives.
- The first step if their ability to identify and include right people with them towards achieving goals. Unlike the traditional method of building strategies and then looking for the right people to carry them out, they take a different route. It’s about getting the right people on board and then deciding on the destination.
- They also do not shy away from facing and accepting brutal truths and realities of data, numbers and situations but at the same time they do not lose hope of a better future.
- They also strive towards aligning consistent efforts towards a goal, rather than giving one massive push they believe in small but firm pushes to bring in the momentum.
- They also exercise their judgment to understand an aspect, in depth and thoroughly, rather than burdening themselves with myriad information.
- They practice and encourage a disciplined approach towards their work life and as visionaries use carefully identified technologies to give their businesses strategic advantage.
With the new concept of Level 5
leadership we come back to an age old question, can Level 5 leadership be
learnt, if yes then how. According to Collins it is farfetched to suitably see
whether it can be learnt or not but he surely identifies two categories of
people, one who have the Level 5 Leadership in them, dormant, latent or
unexpressed and others who do not have it.
So leaders who cannot look beyond
their personal role, fame, achievements etc can hardly become Level 5 leaders.
Only when they can put the larger good ahead of them, they transcend to the
next level. This transition is not general but can be brought by some tragic
accident, near death experiences or a life changing incident, as came across by
Collins in his research. It would be appropriate to mention the name of M.K.
Gandhi to understand it better. For Gandhi who had lived a comfortable life
with a law degree from England had no experience of being oppressed by the
ruling class until he was thrown out of a train despite carrying a first class
ticket. His transition began from there, which later made him actively
participate in the Indian Freedom Struggle.
Situational Leadership - Meaning and Concept
Leaders are essentially people who
know their goals and have the power to influence the thoughts and actions of
others to garner their support and cooperation to achieve these goals. In-case
of leaders these goals are rarely personal and generally to serve the larger
good.
Ever since man was a hunter gatherer
and lived in closely knit groups, they had leaders who led the hunting
expeditions and took greater risk than the rest of the group members. In turn
they were bestowed with larger share of hunting, respect and a higher position
in the group. With changing times, how leadership is perceived has also
changed, but, it remains an important aspect of social fabric nevertheless.
The initial theories proposed that
leaders are born and cannot be created, there are certain distinct
characteristics possessed by few men which make them leader. However, for the
current discussion we would try and take a closer look at another interesting
theory which was proposed called Situational Leadership Theory. This theory
says that the same leadership style cannot be practiced in all situations,
depending upon the circumstance and environmental context the leadership style
also changes. The pioneers of this theory were Kenneth Blanchard and Paul
Hersey.
The model encourages the leaders to
analyze a particular situation in depth and then lead in the most appropriate
manner, suitable for that situation.
The three aspects that need could be considered in a situation are:
- Employees’ competences
- Maturity of the employees
- Complexity of the task
- Leadership style
In the Situational Leadership model,
the leadership style has been divided into 4 types:
- S1: Telling - Telling style is associated with leaders who minutely supervise their followers, constantly instructing them about why, how and when of the tasks that need to be performed.
- S2: Selling - Selling style is when a leader provide controlled direction and is a little more open and allows two way communication between him/herself and the followers thus ensuring that the followers buy in the process and work towards the desired goals.
- S3: Participating - This style is characterized when the leaders seeks opinion and participation of the followers to establish how a task should be performed. The leader in this case tries creating relationship with the followers.
- S4: Delegating - In this case, the leader plays a role in decisions that are taken but passes on or delegates the responsibilities of carrying out tasks to his followers. The leader however monitors and reviews the process.
It is also represented by a diagram
most often which is below:

The developmental level of follower
is an important indication for a leader to decide the most appropriate
leadership style for them:
- D4 - High Competence, High Commitment - The followers who are identified in this category are the ones who have high competence and high commitment towards tasks to be performed. It might happen so that they turn out better than their leaders in performing these tasks. (For e.g. cricketing legend Sachin Tendulkar playing in the Indian cricket team under the captainship of Mahendra Singh Dhoni)
- D3 - High Competence, Variable Commitment - This category consists of followers who have the competence to do the job but their commitment level is inconsistent. They also tend to lack the confidence to go out and perform task alone. (E.g. President Barack Obama)
- D2 - Some Competence, Low Commitment - In this case, the followers have a certain level of competence which might be sufficient to do the job but they are low on commitment towards the tasks. Despite of having relevant skills to perform the task they seek external help when faced with new situations. (A team member made the trainer for new joiners)
- D1 - Low Competence, High Commitment - This category of followers may not have the specific skill required but they display a high level of commitment towards the task they have to perform, with confidence and motivation, they figure out ways to complete the tasks. (E.g. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, a lawyer by profession who spearheaded the Indian Freedom Struggle)
The above information regarding the
style of leadership and the type of followers sure has a correlation to each
other which forms the basis of situational leadership. So, a situational leader
would try to accommodate his leadership style as per the situation and the
level of competence and commitment of his followers. This information is also
an important aspect to consider when senior leaders act as coaches for their
subordinates in the organizations.
Impact of Situational Leadership on Performance and Motivation
Leaders are role models who influence the culture, values, thoughts and actions of the organization and its people. The leadership style practiced by managers greatly influences the performance and productivity at the work place. The situation leadership model encourages managers to flexibly use their leadership style based on the situation and thus achieve effective results. Both at the middle managerial level where leaders work closely with people and at higher managerial level where leaders are responsible to a number of people, their approach has an impact on the motivational levels of the organization.A leader needs to constantly inform him/herself of the motivational needs of the employees, one of simple factors of success cited in the organizations is a motivated workforce. The 4 leadership style of Telling, Selling, Participating and Delegating proposed in the situational leadership model can be used as per the motivational need of the subordinate. For example, for a senior manager who has been recently recruited and who boasts an illustrious career graph would need more responsibilities and opportunities to prove himself i.e. Delegating to remain motivated. On the other hand a fresher joining the organization may look at more Telling and a little participative approach to keep him/her motivated. A leader has to carefully evaluate and then decide on the right approach for the subordinate.
Situational Leadership has all the more relevance when teams work together especially across functions or locations. In these cases the team members might be physically separated from the leaders and the work situations might rapidly change, in such cases, maintaining the involvement and motivation level of team members becomes important. To create a high performance team that works effectively, the style that the leader would have to choose may be unique for each team.
Apart from this, a leader has to provide a vision to the people; it is the visions which help them direct and redirect their efforts towards it. In the recent times where changes are rapid in the organizations, the leaders have to be fully sensitized to what style would work the best, sometimes they might have to use a combination of styles to address issues effectively. For e.g. for a new change that is being introduced, the initial approach has to be Selling, where people are educated about the change, the next step becomes Telling, where the people have to be instructed as to how the change would be carried out. When the change starts settling in and people adopt it, they style can become Participating, where the people get an opportunity to partner in the change and take it ahead. The last change would then become delegating when the change can now be carried on by the others. The ultimate aim of any leader is to smoothly arrive at a stage where he/she can easily delegate tasks without worrying about its completion or effectiveness.
The leadership style also has a bearing when leaders are to act as mentors and coaches for their subordinates. The learning style of the subordinates can be interpreted in the terms of Telling, Selling, Participating and Delegating. Some subordinates learn when they know exactly what is to be done, some learn when they know the importance of the task, some learn when they understand the how of what is to be done, and ultimately some learn when they are actually allowed to perform the task. When a leader acts as a coach he/she has to keep in mind what works best for the coachee and the fact that what works for one might not work for the other.
Influence of Situational Leadership Styles on Subordinate Development
As we know that the situational leadership theory proposes that a leader needs to change his/her leadership style as per the situation and environment. Leaders also need to consider the level of their followers; to decide on a particular leadership style. Let us now try to explore, whether the leadership style practiced by the leader influences the subordinates at all and if they do then how does it happen?In the organizational context a manager is not just a superior for his team of subordinates but is also their leader. This implies that as a manager he/she has to make sure that the subordinates are working cohesively as a unit to achieve department or function goals, and if a problem arises the manager has to step up and take the responsibility as a leader.
How would a manager ensure that each member and the team collectively are working towards that common goal? Sometimes, the contribution from each member is not equal, some are working and some are not, which often leads to imbalances and negativities in the team and work environment.
It is the leadership style practiced by the manager which to quite an extent is responsible for such a situation to arise. Every team has people who have different level of competence and commitment towards the work they do, some are pro-active and others need to be pushed. In either case, the role of the manager as a leader becomes all the more important where he/she needs to be flexible with the kind of leadership style they can practice with each subordinate.
Let’s try to understand the relationship between leadership styles and subordinate development in a little detail. Recall the four situational leadership styles identified by Hersey and Blanchard. They were:
- Telling
- Selling
- Participating
- Delegating

For a subordinate, who stands at a level D2 where he has some competence but lacks or shows inconsistent commitment, the leader can resort to the Telling style. In this case, the subordinate cannot be relied upon to complete the task without instructions and guidance. For the subordinates who fall into the category of D3 or high competence but variable commitment, the leadership style could be Selling as the leader would have to create a buy in from these subordinates to secure their commitment towards the task. Since they have the necessary competence to do the task, instructions are not required but such subordinates wish to see the value of the work they are doing to get committed to it.
And lastly, if the subordinate fall into the category of D4 where they have both high commitment and high motivation, the leadership style best suited could be Delegating, where the leaders need to understand, acknowledge and appreciate the competence and commitment of the subordinates and entrust them with responsibilities.
Leaders have to be aware of their surroundings and sensitized to the abilities and motivations of their followers/subordinates in order to be able to take effective decisions.
No comments:
Post a Comment