MARKETING MANAGEMENT

The concept reviews the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers and the strategy to use for marketing mix. It also explores the process of understanding, creating and delivering value to targeted business markets and customers.
Marketing Management identifies market opportunities and comes out with appropriate strategies for exploring those opportunities profitably.It has to implement marketing programme and evaluate continuously the effectiveness of marketing-mix. It has to remove the deficiencies observed in the actual execution of marketing plans, policies, and procedures. It looks after the marketing system of the enterprise.
Management is the process of getting things done in an organised and efficient manner. Marketing management aims at efficient operation of marketing activities.
Marketing management smoothen the process of exchange of ownership of goods and services from seller to the buyer. Marketing management, like all other areas of management comprises of the function of planning, organising, directing coordinating and controlling.
Marketing Management – Concepts
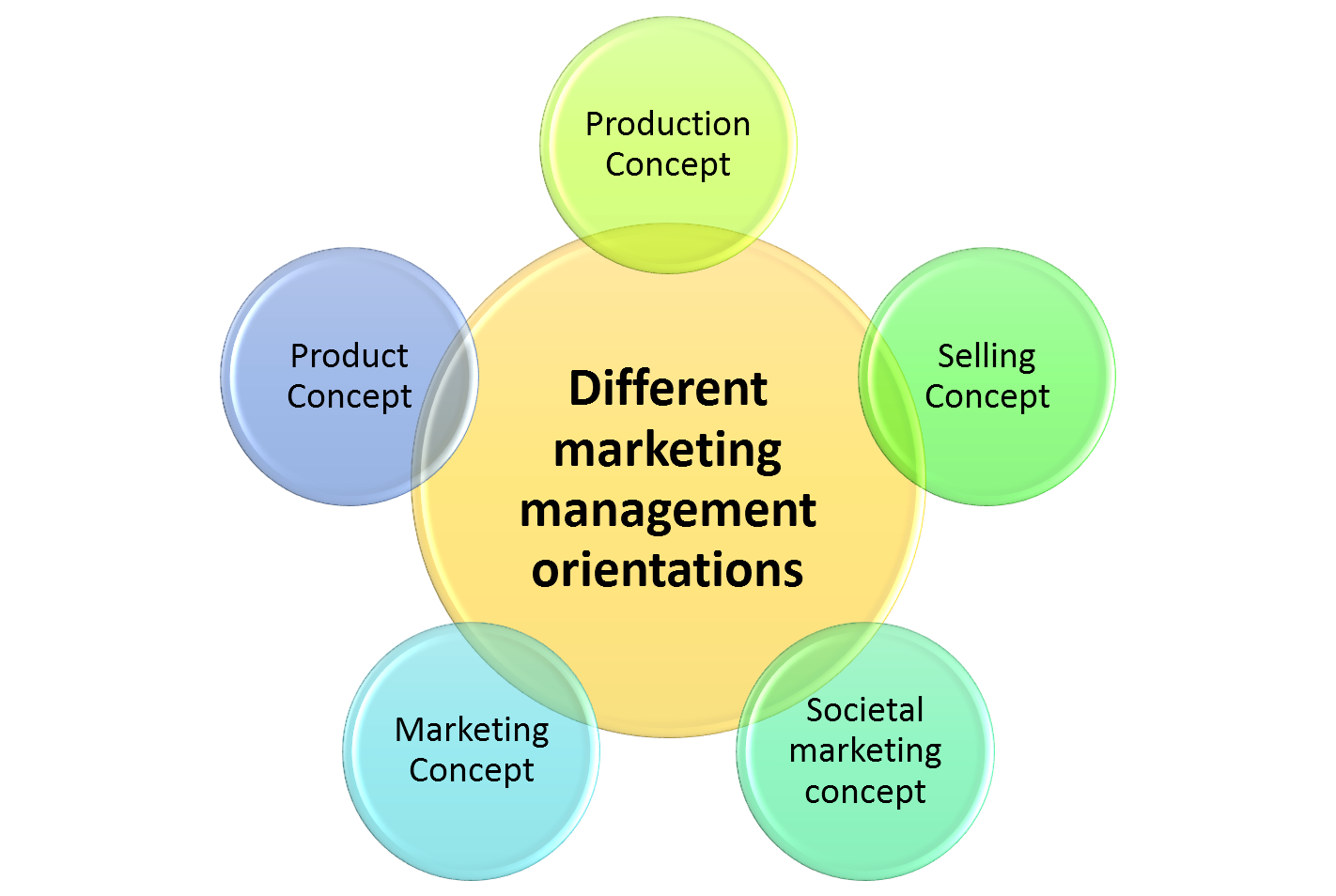
Marketing concept is the philosophy that companies should examine the requirements of their customers and then make decisions to satisfy those needs in a better manner than the competitors.
Today, most of the companies have adopted various marketing concepts, but this has not always been the case. Let us now understand major marketing concepts.
The major marketing concepts are −
1. Production concept
2. Sales concept
3. Marketing concept
Production Concept
According to the production concept, a company should focus on those items that it can produce most efficiently and also focus on creating supply of low-cost items that create the demand for the products.
The key questions that a company needs to ask itself before producing an item are −
Can we produce the item?
Can enough of it be produced?
This concept worked fairly during the 1920s as the items that were produced were largely those of basic necessity and there was a relatively high level of unfulfilled demand. Virtually everything that could be produced was sold easily by a sales team whose task was to complete the transactions at a price fixed by the cost of production. All in all, this concept prevailed until the late 1920's.
Sales Concept
According to this concept, the companies would not only produce the items but would also try to convince customers to buy them through advertising and personal selling. Before producing a product, the key questions were −
Can we sell the item?
Can we account enough for it?
This concept paid little attention to whether the item actually was required. The goal simply was to beat the competition with little focus on customer satisfaction. Marketing was an operation performed after the product was developed and produced and many people came to relate marketing with hard selling. Even today, people use the word "marketing" when they actually mean “sales.”
Marketing Concept
The marketing concept relies upon marketing studies to define market segments, their size, and their requirements. To satisfy those requirements, the marketing team makes decisions about the controllable parameters of the marketing mix.
This concept was introduced after World War II as the customers could afford to be selective and buy only those items that precisely met their changing needs and these needs were not immediately obvious. The key questions changed to −
What do customers actually want?
Can we improve it while they still want it?
How can we keep the customers satisfied?
In reply to these discerning customers, companies began to adopt marketing concepts, which includes −
Focusing on customer requirements before developing a product
Aligning all operations of the company to focus on those needs
Realizing a gain by successfully satisfying customer needs over the long-term
When companies began to adopt this concept, they actually set up separate marketing departments whose objective was to satisfy customer needs. Mostly, these departments were sales departments with expanded responsibilities. While this widened sales department structure can be found in some enterprises today, many of them have structured themselves into marketing organizations having a worldwide customer focus.Marketing Management - Process
Marketing process includes ways in which value can be created for the customers to satisfy their requirements. It is an endless series of actions and reactions between the customers and the companies making attempt to create value for and satisfy the needs of customers.
In marketing process, the situation is examined to identify opportunities, the strategy is formulated for a value proposition, tactical decisions are taken, plan is executed, and results are monitored.
The following four steps are involved in the marketing process −
Situation Analysis
Analysis of the situation in which the company finds itself serves as the basis for identifying chances to satisfy unfulfilled customer needs.
Situational and environmental analysis is done to identify the marketing options, to understand the company’s own capabilities and to understand the surroundings in which the company is operating.
Marketing Strategy
After identifying the marketing options available, a strategic plan is developed to pursue the identified options. An analysis is done and the best available option is chosen; a plan or strategy is made for that option.
Marketing Mix Decisions
At this step, elaborated tactical decisions are made for the controllable parameters of the marketing mix. It includes decisions related to product development, product pricing, product distribution and product promotion.
Implementation and Control
Finally, the marketing plan is executed and the outputs of marketing efforts are monitored to adjust the marketing mix according to the market changes.
This being the final step, it transforms the written or planned strategy into action and the product is presented according to this process.
Marketing Management - Functions
The term functions of marketing management means the main role of this type of management in any organization.
Major Functions of Marketing Management
We need to understand the major functions of marketing management in order to understand and groom our organization. The following are some of the major functions of marketing management −
Selling
Buying and Assembling
Transportation
Storage
Standardization and Grading
Financing
Risk Taking
Market Information
The marketing process performs certain activities as the products and services move from the producer to consumer. All these activities or jobs are not performed by every company.

Nonetheless, it is recommended that they be carried out by any company that wants its marketing systems to function successfully.
Selling
Selling is the crux of marketing. It involves convincing the prospective buyers to actually complete the purchase of an article. It includes transfer of ownership of products to the buyer.
Selling plays a very vital part in realizing the ultimate aim of earning profit. Selling is groomed by means of personal selling, advertising, publicity and sales promotion. Effectiveness and efficiency in selling determines the volume of the firm’s profits and profitability.
Buying and Assembling
It deals with what to buy, of what quality, how much from whom, when and at what price. People in business purchase to increase sales or to decrease costs. Purchasing agents are much tempted by quality, service and price. The products that the retailers buy for resale are selected as per the requirements and preferences of their customers.
Assembling means buying necessary component parts and to fit them together to make a product. ‘Assembly line’ marks a production line made up of purely assembly functions. The assembly operation includes the arrival of individual component parts at the work place and issuing of these parts for assembling.
Assembly line is an arrangement of employees and machines in which each individual has a particular job and the work is passed directly from one employee to the next until the product is complete.
Transportation
Transportation is the physical means through which products are moved from the places where they are produced to those places where they are needed for consumption. It creates locational utility.
Transportation is very important from the procurement of raw material to the delivery of finished products to the customer’s places. Transportation depends mainly on railroads, trucks, waterways, pipelines and airways.
Storage
It includes holding of products in proper, i.e., usable or saleable, condition from the time they are produced until they are required by customers in case of finished products or by the production department in case of raw materials and stores.
Storing protects the products from deterioration and helps in carrying over surplus for future consumption or usage in production.
Standardization and Grading
Standardization means setting up of certain standards or specifications for products based on the intrinsic physical qualities of any item. This may include quantity like weight and size or quality like color, shape, appearance, material, taste, sweetness etc. A standard gives rise to uniformity of products.
Grading means classification of standardized items into certain well defined classes or groups. It includes the division of products into classes made of units possessing similar features of size and quality.
Grading is very essential for raw materials; agricultural products like fruits and cereals; mining products like coal, iron and manganese and forest products like timber.
Financing
Financing involves the application of the capital to meet the financial requirements of agencies dealing with various activities of marketing. The services to ensure the credit and money needed and the costs of getting merchandise into the hands of the final user are mostly referred to as the finance function in marketing.
Financing is required for the working capital and fixed capital, which may be secured from three sources — owned capital, bank loans and advance & trade credit. In other words, different kinds of finances are short-term, medium-term, and long-term finance.
Risk Taking
Risk means loss due to some unforeseen situations. Risk bearing in marketing means the financial risk invested in the ownership of goods held for an anticipated demand, including the possible losses because of fall in prices and the losses from spoilage, depreciation, obsolescence, fire and floods or any other loss that may occur with the passage of time.
They may also be due to decay, deterioration and accidents or due to fluctuation in the prices induced by changes in supply and demand. The different risks are usually termed as place risk, time risk, physical risk, etc.
Market Information
The importance of this facilitating function of marketing has been recently marked. The only sound foundation on which marketing decisions depend is timely and correct market information.
The importance of this facilitating function of marketing has been recently marked. The only sound foundation on which marketing decisions depend is timely and correct market information.
Marketing Management – Environment

Marketing environment can be defined as the composition of all the factors affecting the market, marketing system and functions related to marketing.
Types of Layers
There are different layers of marketing environment. Each layer has special characteristics. Marketing environment has the following four layers −
Organizational environment
Marketing environment
Macro environment
Micro environment
Organizational Environment
An organizational environment consists of forces or institutions surrounding an organization that affect performance, operations and resources. It includes all of the key elements that exist outside of the company's boundaries and have the potential to affect a portion or all of the organization.
Marketing Environment
The market environment is a marketing term that refers to factors and forces that affect a company's behavior.
By the term company’s behavior, we mean the company’s ability to build and maintain successful relationships with customers, clients and all the people related to it.
Macro Environment
The term macro means large. Macro refers to large factors or vital factors like social factors, for example, male-female ratio, social changes, new lifestyle, or arrival of new thought. Examples of economic factors are per capital income, balance of payment, balance of trade, inflation rate, and gross domestic product.
Other factors like geographical, cultural, political, demographical and legal factors such as competitions and technology are also included in this environment.
Examples − Geographical distribution, distance from market, age, sex, literacy etc., cultural differences, cultural change, arrival of a new tradition, government decision making, new plans, programs & policies, government support, political disturbances and so on.
Micro Environment
Here the word itself describes the meaning − micro means small. So, micro environment is a composition of small factors, inside factors/nearer factors like customers, mediators like wholesaler, retailer, supplier, other stakeholders who demand something from the organization, i.e., shareholders, debenture holders, creditors, debtors, moneylenders, etc.
Micro environment also involves factors like working conditions, employees, purchase groups, local community and pressure groups.

Michel Porter is known for his marketing and management thoughts and skills. He contributed many valuable theories to the modern marketing management. Here we are going to see Porter’s five forces model theory.
The model includes the following five forces −
Potential entrants
Bargaining power of suppliers
Bargaining power of buyers
Industry competitors
Threat of substitutes
Potential Entrants
It refers to the addition of new competitors in the existing market. As we know, for each product we have different options or we have different companies offering the same product with some slight variation in price, item etc.
Thus, potential entrants refer to the entrance of new companies in the market and ways to deal with it.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
A supplier or producer is the one who produces the product desired or required by the market. The supplier is not necessarily a single person; it can be a group, company or anything.
The function of a supplier is to design products as per the requirement of the client, company, market and society.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Buyer or consumer is the one who swaps the product designed by the supplier as per the demand of the buyer with some valuable commodity.
The function of a buyer is to be precise in what actually is needed and purchase it from the supplier, for example, buying a car or any other product.
Industry Competitors
The companies competing with other companies within the same market are known as industrial competitors.
Threat of Substitutes
The threat of a substitute paves way for competition in an industry. The threat of substitution in an industry affects the competitive environment for the firms in that industry and influences those firms’ ability to achieve profitability. The availability of a substitution threat effects the profitability of an industry because consumers can choose to purchase the substitute instead of the industry’s product.
Marketing Management – Planning

Marketing planning is the process of improvising a marketing plan incorporating overall marketing objectives and goals and designing strategies and programs of actions to achieve those objectives.
Marketing planning includes setting objectives and targets and allocating those targets to people responsible to achieve them. It also includes careful examination of all strategic issues, including the business environment, the market itself, the corporate mission statement, competitors and organizational capabilities.
Marketing planning is a sequence of stages that are usually followed in a format. Companies can adopt a marketing plan to suit the situations and their requirements. Marketing planning process includes both the development of objectives and specifications of how to achieve those objectives.
Let us now discuss the components of a marketing plan.
Mission
It is the reason for which a company exists. Mission statement is a direct statement that shows why a company is in business, provides basic guidelines for further planning, and organizes broad parameters for the future.
Most of the useful mission statements encourage staff and customers.
Corporate Objectives
Objectives are the set of goals to be achieved within a specified timeframe. Corporate objectives are essential goals the company as a whole wishes to achieve within a given timeframe such as one or five years.
Marketing Audit
Marketing audit helps in examining and evaluating the marketing strategies, activities, problems, goals, and results.
It is done to check all the aspects of business directly linked to the marketing department. It is done not only at the initial state of marketing planning process but also at a series of points during the execution of plan.
SWOT Analysis
The information collected through the marketing audit process is used for the development of SWOT Analysis. It is an analysis of the company's marketing efforts and its strengths, weaknesses, options, and warnings related to marketing functions.
Marketing Assumptions
A good marketing plan depends on in-depth customer understanding and knowledge. However, it is not possible to know everything about the customer, and many different things are assumed about the customer. Example: Assumptions of who the target buyers might be.
Marketing Objectives and Strategies
After identification of options and challenges, the next step is to develop marketing objectives that mark the end state to achieve.
Marketing strategies are formed to achieve the marketing goals and objectives. They are formed to determine how to achieve those target points.
Forecast the Expected Results
Marketing managers have to predict the expected results. They have to project the future numbers, features, and trends in the target market.
Without proper forecasting, the marketing plan could have impractical goals or fall short on what is promised to deliver.
Create Alternative Plan
An alternate or substitute marketing plan is created and kept ready to be executed in the place of the primary marketing plan if the whole or some part of the primary marketing plan is dropped.
Marketing Budget
The marketing budget is the process of documenting the desired costs of the proposed marketing plan.
One common method is to allocate the marketing budget depending on the percentage of revenue. Other methods are comparative method, all you can afford, and task method.
Implementation and Evaluation
At this stage, the marketing team is all set to put their plans into action. This may include spending money on advertising, launching new products, interacting with potential new customers, opening new retail outlets etc.
A marketing planning process is required to be verified and updated on a regular basis.
Marketing Management - RESEARCH

Marketing research can be defined as the development, interpretation and interaction of decision-oriented information to be used in all phases of marketing process.
Managers require information in order to introduce products and services that create value in the mind of the customer. But the perception of value is a rational one, and what customers prioritize this year may be quite different from what they prioritize next year.
As such, the elements that create priority cannot simply be deduced from common knowledge. Rather, data must be collected and examined. The goal of marketing research is to ensure the facts and direction that managers need to make their more essential marketing decisions. However, to increase the benefit of marketing research, those who use it need to understand the research process and its limitations.
Global Market Research
Global marketing is the process of adjusting an enterprise's marketing strategies to adapt to the situations in other countries.
Suppose we have a widget we would like to sell in Europe and we are developing our marketing plan. We need to make some strategic decisions like market segmentation, localization, strategic planning and so on.
Global market research is brings clarity on the following points −
Decide whether to go overseas
Get an idea about the competitive strength of global market
Decide which market to enter with better information
Provide knowledge about how to enter global market.
Help in formulating marketing schedule, product decision, promotion, product pricing & selection of distribution channel.
Help in marketing companies.
In short, we can conclude that global market research is necessary when one wants to expand the business globally, as to other countries.
Marketing Research Vs. Market Research
Market research precisely deals with collecting information about a market's size and trends whereas marketing research covers a range of activities and it may include market research.
Marketing research is a more general synchronized process that can be used to a variety of marketing problems. Marketing research by itself does not deal with marketing decisions, nor does it guarantee that the company will be successful in marketing its products. However, when conducted in a synchronized, systematic, analytical, and objective manner, marketing research can minimize the uncertainty in the decision making process and increase the probability and magnitude of success.
Organizational buying behavior (OBB) can be defined as the process of how companies or organizations buy goods and services. The buying behavior of an organization is a step-by-step process. It is not a one-night journey to launch a product and change the market behavior. It is a time-consuming procedure and is done in a synchronized manner.

OBB plays a very important role in the modern marketing concept. It is a well-defined and properly maintained marketing process with wide contact between the buyer and seller.
Characteristic Features of OBB
The major features that decide the buying behavior of an organization as a whole can be learnt from the following points −
It is an analytical process.
Number of individuals engaged is more.
It handles large quantity marketing.
Purchase criteria are precise and well defined.
There is broad contact between buyers and sellers
It includes user, influencer, decider, buyer and gatekeeper.
After seeing these features, we have an idea of the concept of organizational buying behavior. It is not always the money that decides what to buy but some other features apart from money are also very important.
Determinants of OBB
Determinants of OBB can be defined as the agents that originated OBB. There are two determinants of the buying behavior of an organization.
Organizational factors like objective, technological capacity, company’s structure, human resource criteria and many more.
Psychological factors like perception, motivation, attitude, belief and many more.
After having a quick look on these determinants or agents of buying behavior of a firm, let us look at the participants of OBB.
Participants of OBB
Participants of OBB are the people involved, responsible and answerable in the buying behavior of an organization.
We can see the following seven different types of participants in OBB −
Initiator − The one who initiates the buying of the product.
Influencer − The one who influences others or, say, the organization, to buy a product.
User − The one who is going to use the product.
Decider − The one who decides if the product should be used.
Approver − The one who permits or approves the use of the product.
Buyer − The one who is going to buy the product.
Gatekeeper − The one who watches the buying behavior.
Participants in OBB are responsible for their fields respectively.
Steps of OBB
Organizational buying is not an easy activity as most people think of it. The process of OBB consists of the following steps and each one is very important and affects the next one −
Problem recognition
General need
Product specification
Searching for potential supplier
Value analysis
Vender analysis
Order routine specification
Multiplicity surrounding
Performance Reviews
Stages in Organizational Buying Process
Following are the stages in the organizational buying process −
Problem Recognition − It is the first stage of the business buying process. In this stage, someone in the organization recognizes an issue or need that can be met by acquiring a good or a service.
General Need Description − At this stage of business buying process, the organization briefs the general features and quantity of a needed product.
Product Specification − At this stage of the business buying process, the buying company decides on the item and specifies the best technical product features for a needed item.
Value Analysis − This stage involves an access to cost reduction, in which elements are studied carefully to select if they can be redesigned, standardized or made by less costly methods of production.
Supplier Search − At this stage of the business buying process, the consumer tries to find the best sellers.
Proposal Solicitation − In this stage of the business buying process, the buyer invites qualified suppliers or producers to submit the proposals or options they have.
Supplier Selection − In this stage of the business buying process, the buyer reviews plans and chooses a supplier or suppliers.
Order-routine Specification − This is the stage of the business buying process in which the buyer writes the final order with the selected supplier(s), enlisting the technical specifications, quantity required, expected time of delivery, return policies, manufacturing date and warranties.
Performance Review − In this stage of the business buying process, the buyer rates his satisfaction with suppliers, deciding whether to continue, develop or drop them.
Types of Organizational Market
In order to facilitate the buying behavior of a market, we divide the organizational market into these four types.
Product Market
Producers purchase items and services and transform them into a sellable product, which they sell to their customers for the purpose of gaining profit; this is known as product market. Examples of producers are farmers, manufacturers and construction companies.
Retailer Market
The market for the sale of products or services to consumers instead of that to producers or intermediaries is known as the retailer market. For example, a shoe store sells to people who will most likely wear the shoes. It does not include the sale of the shoes to other stores who will resell them. The retail market contrasts with the wholesale market.
Government Market
The market where the consumers are national, state, and local governments is known as the government market. Governments buy both products and services from the private sector.
Governments purchase the same types of products and services as the private sector consumers, in addition to some more exotic products such as aircraft carriers, fighter jets, tanks, spy satellites and nuclear weapons.
International Market
The market where the marketing principles are applied to more than one country is known as the international market.
Market of product is decided by the product type. A product can be introduced to more than one market or the product can be specifically introduced at any single market type.
Market segmentation can be defined as the subdivision of the market into compatible subsections of customers where any subsection may be selected as a market target to be reached with a unique marketing mix.

For example, Hindustan Unilever (HUL) produces a variety of products for different classes such as Surf Excel for higher class, Rin for middle class and Sunlight/Wheel for the lower class.
Objectives of Marketing Segmentation
The main objective of marketing segmentation or the goals to be achieved through marketing segmentation can be understood through the following points −
To label potential customers
To avail additional privileges for their customers
To acknowledge the convenient place to purchase
To pay additional benefits willingly
To pay proper attention to some precise area
To ensure proper database marketing usage
To acknowledge real competition in the market
To enhance productivity
These are the objectives an organization should keep in mind in order to design the marketing mix and increase its promotion. Let us move forward with the topic and have a look on the importance of market segmentation.
Importance of Segmentation
To achieve the objectives stated above, one has to clearly know the need of market segmentation in the first place. Following are some points outlining the importance of market segmentation.
It promotes proper selection of target market.
It assists planning and marketing exercises.
It aids the tapping of market.
Marketing effort is made more effective.
It assists in accessing the strength and weakness of the company.
It assists in effective usage of marketing resources.
It balances proper coordination between the customers and the company.
Based on these points of importance of market segmentation, we will further look at the levels of market segmentation.
Levels of Market Segmentation
The level of marketing segmentation is dependent on the marketing plan of the marketer and the product attributes. There are four different levels of market segmentation.
Segment marketing
Individual marketing
Niche marketing
Local marketing
Segment Marketing
In segment marketing, we divide the entire marketing into a bunch of customers with respect to some common characteristics. That common characteristics may be taste, preference, choice etc. Segmenting this market is a very complex process as there are no criteria for the above attributes.
Individual Marketing
In this case, the customers are targeted individually by e-mail, SMS, calls etc. However, in order to make this marketing successful, we have to reduce the degree of heterogeneity.
Niche Marketing
In this type of segmentation, the small markets are targeted taking into consideration customer taste, preference, income and purchasing power.
In this type of market, we have to care for the bargaining power, the discounts, free gift, bonus points, free delivery, lucky coupons and post purchase voucher.
Local Marketing
In this type of segmentation, generally the local markets are targeted.
The organizations try to create patriotism in the mind of the customer by following the slogan “See global, use local”. Again they take help of low-cost advertisements, low transportation costs, frequent delivery, speedy services etc.
Marketing segment are determined depending on the targeted consumer groups for particular products.
Steps in Market Segmentation
Segmentation is the process of creating small portions within a broad market to choose the right target market for various brands. Market segmentation assists the marketers to devise and execute relevant strategies to sponsor their products amongst the target market.
A market segment consists of people who have identical choices, interests and preferences. They generally think on the same lines and are biased towards similar products. Once the enterprise selects on their target market, they can easily codify strategies and plans to make their brands fashionable amongst the consumers.
Identify the Target Market
Identifying the target market means choosing the group of audience who could be a potential customer for the product. By identifying the target group, the marketing strategies can be prepared and products can be shaped.
For example − Different segments of cars are targeted at different consumer groups like the SUV for consumer who likes adventure and prefers outdoor road trips and the Sedan for luxury seeker consumer.
Identify Expectations of Target Audience
Expectations of different audience vary as per their requirement from the product. The demand and requirement of the target consumer changes and the company should keep a track of it and change its strategy as needed. For example, Instant noodles are designed for consumers who don’t have much time to cook.
Create Subgroups
Creation of subgroup specifies the group it is targeted at and consumers from that group can easily relate to the product. This gives the product an edge in market over other products. For example, Face wash has created subgroups such as men and women and advertisements are made accordingly.
Review the Needs of the Target Audience
It’s important to review the needs of the target audience for upgrading the product or shaping the product as per the requirement of the audience. Consumers’ demands change from time to time and the product has to adapt as per the changes in demand.
Name Your Market Segment
Segments should be given an appropriate name so that the products in that segment can be easily identified.
For example − Stores have segments like Boy, Girl, Men, Women, etc., which gives the idea of the products in that segment.
Marketing Strategies
Marketing strategies are meant to promote and advertise the product. They change as per the segment. Advertisements should be for the target audience so that there is a link between the product and the consumer.
Review the Behavior
The review of target consumer gives an insight into the product. Demands vary differently at a particular time of the year and perception of product changes. By taking review of these behaviors, marketing can be planned accordingly.
Size of the Target Market
It’s important to acquire information about the market size and have relevant data for sales planning and forecasting. These steps have to be considered for segmentation of marketing and targeting the product at the potential customers.
Marketing Management - Branding of a Product
Branding can be the name, logo, concept, etc., which differentiate the product or service from the other competitors in the market.
Reasons for Branding
Branding is aimed at promoting your own product. Let us now see why branding a product is essential.
It makes the promotion process easy.
It increases the rate of success in advertising.
It creates an image of the product in customers’ minds, which he/she can relate to.
Brand signifies the organization.
Brand creates product loyalty and stabilizes sales.
It differentiates the product from other competitors in market.
It makes the introduction of a new product easier.
Branding creates a difference from other products, which helps to tackle price competition.
Branding of a product has many upsides; by creating a brand, the product can be stabilized in the market for a longer duration.
Branding Strategies
Branding strategy can be divided into the following two types −
Producer strategy
Middleman strategy
Producer Strategy
The following need to be considered for producer strategies −
Marketing under producer’s brand
Developing a market preference for branded parts or materials
Marketing the product under a renowned middleman brand
This strategy is used by the companies or manufacturers to build a brand.
Middleman Strategy
In this strategy, the manufacturer uses a known distributor brand to advertise the product.
It is the middlemen or distributor brand policy.
It is used by companies without adequate finance for advertisement and promotion.
This can be an advantage to the producer in market.
Positioning a Brand
Positioning a brand means occupying a unique place in the minds of the consumers. The following are the various ways for positioning a brand −
Taking benefit from a trending situation
Connecting various uses
Positioning according to consumer lifestyle
Advertising the benefits
Accruing a competitive position
Benefits offered by the product
Positioning a brand creates an image in the customers’ minds, which one can relate to. It increases the sales of the product.
Marketing Management - Brand Equity
Brand equity can be described as the value of a well-established brand name. A product of a popular brand can generate more revenue as compared to an unknown brand. Consumers have a perspective that a product from well know brand will be better in terms of quality than others. This gives an advantage to a branded product over an unknown product.
Elements of Brand Equity
Brand equity valuation is difficult and doesn’t have any basic criteria. Some of the elements associated to it include −
Consumer loyalty
Awareness of brand
Quality of product
Association with brand
Proprietary assets owned by the brand
Elements of brand equity add a value to the brand; a successful brand has all the elements of brand equity.
Brand Benefits
A brand has various advantages compared to unknown products. Some of the benefits are as follows-
It increases customer confidence in purchasing decision
It increases efficiency and effectiveness of advertisement and promotion
Brand loyalty is increased
Products can be priced higher for bigger margin and higher Return On Investment (ROI)
Extension of brand
Leverage in trade
Unique position of brand
Packaging
Packaging is a method used to protect the product from external factors during transportation or storage. Depending of the nature of product, the packaging can differ.
At the same time, packaging creates a first impression on the consumer so it should be designed accordingly.
Characteristics of Packaging
The characteristics or different features of packaging can be listed as follows −
Attractive packaging
Identity of product
Development
Sustainability of product
Looks genuine
Reveals image of brand
Packaging gives an overview of the product so these characteristics should be considered during the design of packaging.
AIDAS Formula
AIDAS theory is a very popular marketing technique. It states that a consumer goes ssthrough the following five stages before showing satisfaction for a product.
A − Attention
I − Interest
D − Desire
A − Action
S − Satisfaction
These stages are to be evaluated and kept in perspective during the packaging design of the product.
Packaging Strategies
The design of packaging can provide an advantage in the market over similar category product. The following are the different strategies for effective packaging −
Packaging of product line
Multiple packaging
Changing the package
Proper execution of packaging strategies can increase the attractiveness and durability of the product.
Labeling
Labeling is the process of marking an identity on the product. The information used for labeling contains the following details −
Name and address of the manufacturer
Name and address of the distributer
Maximum Retail Price (MRP) of the product
Manufacturing date of the product
The method used to manufacture
Ingredients used
Precaution details
Quantity
Expiry date
The information provided in labeling is important because of various reasons like tracing the origin of the product, genuinity of product, etc.
Product Mix
Product mix refers to all the products offered by a particular company. As an example, Reliance Industries has products like cellular service, power, entertainment, etc. Hence, a strategy should be planned such that the uniqueness of the product can be established.
Positioning the Product
It includes positioning in relation to competition, positioning with attributes, and positioning in relation to price and quality of other products in the segment. The product has to be positioned as per these factors in their respective sectors.
Product Mix Expansion
It includes Product depth and product line. These are the dimension of the product mix. It depends on the number of products manufactured by a company.
Planned Obsolescence
Planned obsolescence is a strategy to create space for a new product with the help of advertisements showing an existing product to be out of date or fashion. This strategy is therefore considered controversial. However, it creates a void, which can be filled with a new product satisfying the thirst of newness.
Planned obsolescence is of the following two types −
Technological obsolescence
Style obsolescence
These strategies are used to create a void for a newer product.
5 Successful Marketing Techniques
1. Keep Adding Something New
2. Become a Valuable Resource
3. Separate Yourself from Your Competition
4. Promote the End Result
5. Anticipate Change
Five killer marketing management team strategies
1. Prioritise a content strategy
2. Employ the right staff
3. Launch a social media campaign
4. Use a project management tool
5. Always budget for marketing
22 Modern Marketing Techniques That Cost Time, Not Money
♣ Get Links From Your Service Providers
♣ Search For Unlinked Mentions
♣ Host a Webinar
♣ Cross-promote
♣ Be a Blog Commenter
♣ Help a Reporter Out
♣ Network in Person
♣ Run a Contest
♣ Build a Referral Program
♣ Tweet Up a Storm In Your Niche
♣ Upsell Your Existing Customers
♣ Get Cozy With Niche Influencers
♣ Claim a Hashtag
♣ Get More Email Addresses
♣ Get More User-Generated Content
♣ Talk to Your Fans
♣ Produce High-Quality Press Releases
♣ Hack Craigslist
♣ Blog
♣ Guest blog
♣ Create a LinkedIn Group
♣ Give Free Help to Others
8 Types of Marketing Strategies
Points to ponder for marketing
1. Define the target population
2. Test your audience
3. Consider marketing strategies
4. Evaluate those strategies
» Paid advertising
» Cause marketing
» Relationship marketing
» Undercover marketing
» Word of mouth
» Internet marketing
» Transactional marketing
» Diversity marketing
10 Modern Marketing Skills
HARD SKILLS
1. Data analysis.
2. Writing and content creation
3. SEO
4. Social media
5. Technological proficiency
SOFT SKILLS
1. Flexibility
2. Intuition
3. Emotional intelligence
4. Collaboration
5. Curiosity
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/marketing-skills-list-2062431-final-5b74a69646e0fb00504dc09a.png)
7 Ps of Marketing
![]()






4 comments:
Nice article. Also read about Marketing Mix.
Nice article on marketing management.
Marketing management plays a pivotal role in driving business success by aligning strategies with customer needs and market trends. Professionals looking to sharpen their skills can benefit immensely from events like the Marketing Management Seminar and Master Class, which offer insights into the latest tools and techniques. With a focus on innovation and strategic thinking, mastering marketing management ensures businesses stay competitive and achieve sustainable growth in today’s dynamic marketplace.
An excellent breakdown of marketing management and its evolving concepts! As Kotler and Keller rightly point out, delivering customer value is key—and in today’s digital landscape, that means being visible where customers search first: Google. That's where SEO (Search Engine Optimization) becomes essential.
If you're a business in Bangladesh looking to grow online visibility, attract qualified traffic, and convert leads, then investing in professional SEO is no longer optional—it's vital. At SEO Services Bangladesh, we specialize in helping local and global businesses achieve just that through result-driven SEO strategies tailored to your market segment.
Post a Comment